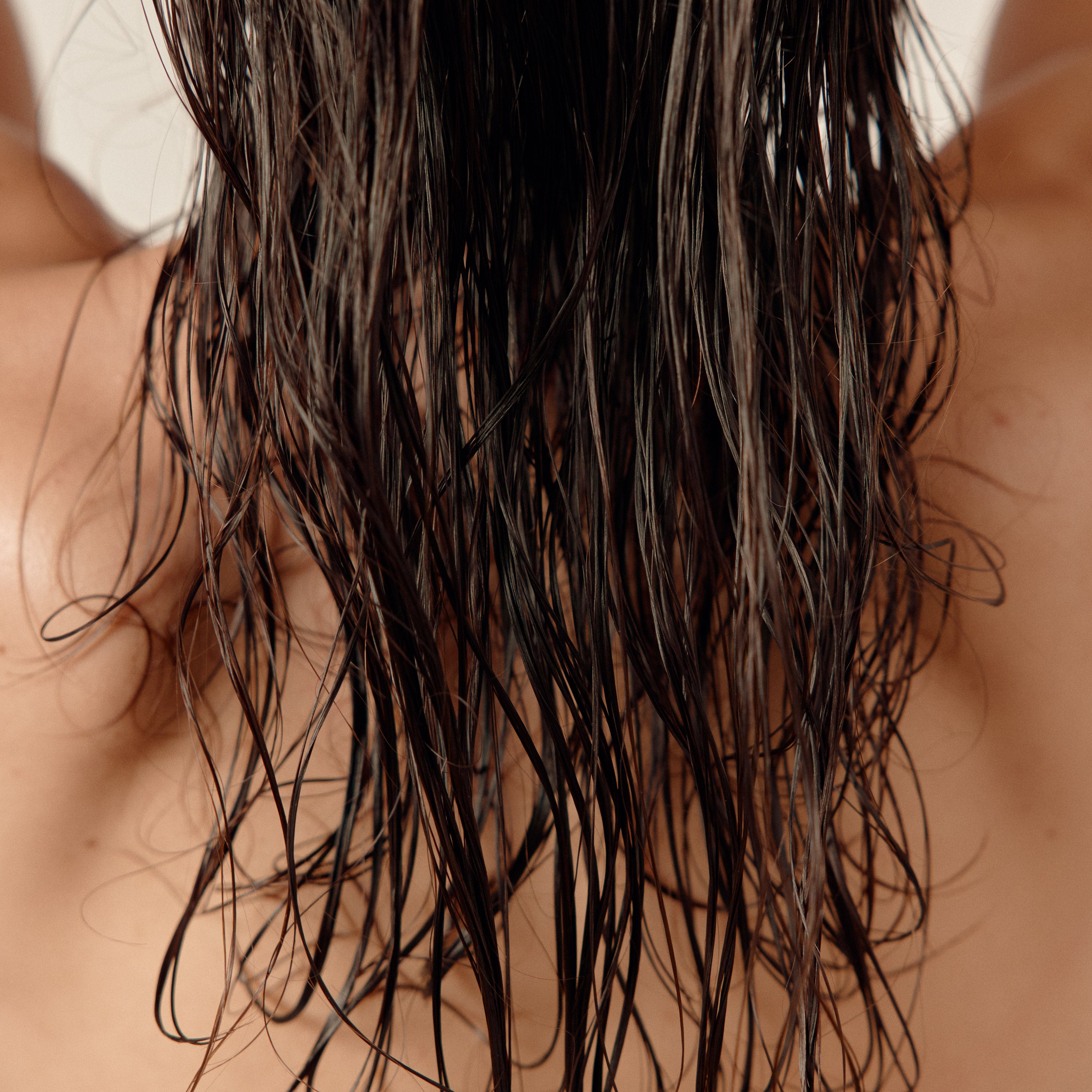

Female hair loss
Hair loss related
to Inflammation
Hair loss related to inflammation is an often overlooked but fairly common phenomenon.
When the scalp becomes inflamed, whether due to irritation, allergies, or certain illnesses, it can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle.
[ 1 ]
Understanding the mechanisms
Some hair loss is caused by inflammatory processes that directly affect the scalp and hair follicles.
When inflammation occurs, the immune system sometimes mistakenly attacks follicle cells, causing damage.
This reaction causes an interruption of the normal hair growth cycle , with a shortened growth phase ( anagen ) and an increased resting phase ( telogen ), which causes premature hair loss.
These inflammatory phenomena can be triggered by autoimmune diseases (such as alopecia areata), scalp infections (mycoses, folliculitis), or reactions to certain products or irritants .
[ 2 ]
The numbers
of the world's population is affected by alopecia areata during their lifetime
which corresponds to approximately 160 million people.
of the world's population is affected by seborrheic dermatitis
Sources:
Mirzoyev, SA, Schrum, AG, Davis, MDP, Torgerson, RR, & McEvoy, MT (2014). Lifetime incidence risk of alopecia areata estimated at 2.1% by Rochester Epidemiology Project, 1990–2009. Journal of Investigative Dermatology , 134(4), 1141–1142. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2013.464
Bernard, T. (2021). Seborrheic dermatitis: literature review of a general medicine pathology [Doctoral thesis in general medicine, Université Côte d'Azur]. HAL. https://dumas.ccsd.cnrs.fr/dumas-03451572v1
[ 3 ]
Recognize the signs
Here are the main forms of hair loss associated with inflammatory causes:
ALOPECIA AREATA
Type of hair loss and characteristics: clear, localized hair loss, forming round or oval patches without visible inflammation. Hair falls out quickly, leaving areas completely bald.
Causes: autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks hair follicles.
Common Triggers: stress, infections, genetic factors, immune imbalances.
SCARRING ALOPECIA
Type of hair loss and characteristics: permanent hair loss with destruction of follicles, irreversible bald areas often with inflammatory signs (redness, scabs).
Causes: chronic inflammation, infections, autoimmune diseases, scalp trauma.
Common Triggers: severe dermatitis, lupus, burns, radiation.
SEBORRHEIC DERMATITIS
Hair loss type and characteristics: moderate diffuse hair loss associated with red patches, oily scales and itching. Hair becomes brittle and thinning.
Causes: inflammation linked to excessive proliferation of yeast (Malassezia) and excessive secretion of sebum.
Common Triggers: stress, humidity, heat, hormonal factors.
SCALP PSORIASIS
Type of hair loss and characteristics: progressive and permanent recession of the hairline and temples, with inflammation and scarring. The skin may appear smooth and shiny.
Causes: autoimmune, chronic inflammation leading to destruction of follicles.
Common Triggers: unknown, suspected hormonal and environmental factors.
FRONTAL FIBROSING ALOPECIA
Type of hair loss: progressive and permanent hair loss at the frontal hairline (forehead) and often at the temples.
Causes: the exact cause remains poorly understood (autoimmune, hormonal and environmental mechanisms are thought to be involved).
Common Triggers: hormonal changes, cosmetic products containing UV filters or chemical agents, significant stress, drug factors (e.g. anti-inflammatories, hormone therapy), environmental exposure.
[ 4 ]
Why it is important to act
When these inflammatory diseases are not treated promptly, hair follicles suffer irreversible damage, leading to permanent scarring alopecia. The later treatment is initiated, the greater the risk of follicle destruction.
Consult a dermatologist: an accurate diagnosis is essential to identify the cause of the inflammation and offer appropriate treatment (corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, antifungals, etc.).
Adopt appropriate hygiene: the use of gentle, anti-inflammatory shampoos can help limit scalp irritation. Stress management , healthy diet .
YOUR TAILORED ROUTINE
[ 5 ]
A WORD FROM THE FOUNDERS

Marie
Co-founder of HACT
In summary
Link between inflammation and hair loss
Exposure to irritants or aggressive factors, or autoimmune diseases
Stress, infections, immune imbalances, burns or radiation

Triggering of local chronic inflammation
Defense reaction: release of inflammatory mediators, edema, oxidative stress around the follicle

Alteration of the follicular environment
Disruption of circulation, nutrient supply and the hair cycle

Weakening of the follicle and hair loss
The hair falls out prematurely (effluvium) or the follicle is destroyed (cicatricial alopecia)











