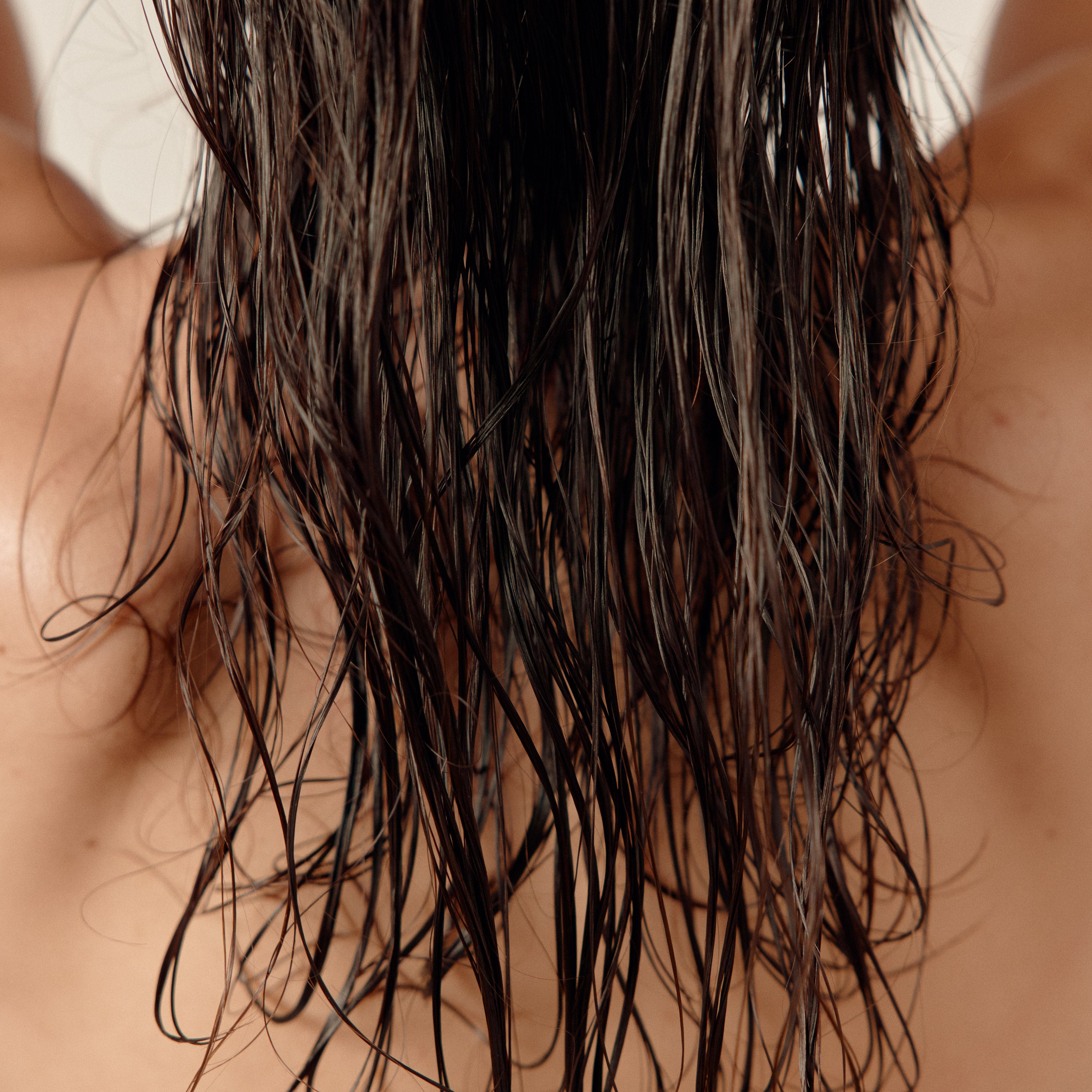

Female hair loss
Hair loss related
to Contraceptive pill
Many women experience hair loss when starting or stopping the birth control pill.
This is due to the significant hormonal changes it causes in the body.
[ 1 ]
Understanding the mechanisms
The birth control pill works by altering the body's hormonal balance. These changes, particularly in estrogen and progesterone , can directly influence the hair growth cycle.
This is because hair follicles have hormonal sensors that are sensitive to changes in hormones.
During the taking
Some combined estrogen pills, due to their estrogen content, can prolong the hair growth phase and reduce hair loss. On the other hand, pills containing progestins with androgenic activity (a "masculinizing" effect) can promote follicle miniaturization and cause hair loss in women sensitive to androgens.
When it is stopped
Depending on the pill, when the pill is stopped, the body experiences a sudden drop in estrogen. This can lead to a temporary hormonal imbalance, often with an androgen rebound effect. This relative spike in androgens can cause sudden but temporary hair loss, called telogen effluvium.
.
In the long term
In women genetically predisposed to androgenetic alopecia, certain pills can accelerate the onset of this condition. Either by masking the hair loss for years (thanks to estrogen), or by triggering or worsening it when they are stopped or replaced with a more androgenic pill.
[ 2 ]
The numbers
of women experience temporary hair loss after stopping the birth control pill
women with a progestin-based hormonal IUD have observed hair loss
Sources:
Chang, F.-LC (2019, November). Telogen effluvium. DermNet NZ . https://dermnetnz.org/topics/telogen-effluvium
(2005). International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics .
[ 3 ]
Recognize the signs
COMBINED ESTROGEN-PROGESTIN PILLS
Composition: estrogen + progesterone
Type of hair loss: diffuse hair loss over the entire scalp when stopped: finer hair, loss of uniform density.
Causes: while taking estrogen, it prolongs the hair growth phase. When it is stopped, the sudden loss of estrogen causes reactive hair loss (telogen effluvium).
Common triggers: stopping after several years of taking the pill, or changing pills.
PROGESTERONE ONLY PILLS
Composition: only progesterone
Type of hair loss: finer hair, diffuse loss on the crown of the head or around the forehead. No completely bald areas, but a density that gradually decreases.
Causes: when taken, some progestin-only pills have an androgenic effect: they increase the activity of DHT (derived from testosterone), a hormone that shrinks hair follicles and accelerates their miniaturization.
Common triggers: starting or changing the pill in women sensitive to androgens, or with a predisposition to androgenetic alopecia.
[ 4 ]
TAKE BACK CONTROL
If you experience hair loss after taking or switching pills, start by identifying the type of pill and its potential effects. Then, talk to your healthcare professional to adjust your contraception if necessary.
To limit the progression of hair loss, it is essential to stimulate the scalp daily to promote blood circulation. Good circulation can prolong the hair growth cycle and strengthen the vitality of the follicles.
When stopping the pill, using a DHT blocker can also limit the impact of this hormone on the follicles, slowing their miniaturization and preserving hair density.
The HACT routine was designed specifically to address this type of problem.
YOUR TAILORED ROUTINE
[ 5 ]
a word from the founders

Julie
Co-founder of HACT
In summary
Link between contraceptive pill and hair loss
Modification of natural functioning
In some women, depending on the composition of the pill, it can cause gradual thinning or diffuse loss

When stopping the pill
Sudden cessation of synthetic hormone intake

Sudden hormonal drop
The body has to relearn how to produce its own hormones, which creates a hormonal imbalance

Increased sensitivity of follicles
Hair follicles, suddenly exposed to a spike in androgens or a drop in estrogen, may react by prematurely entering the resting phase

Hair loss
Post-pill telogen effluvium: diffuse hair loss, often 2 to 4 months after stopping, sometimes accompanied by a return of the underlying androgenetic alopecia if it was masked
















